Introduction:
When it comes to enameled wire, a term that often arises is AWG. What does AWG stand for in enameled wire? AWG, which stands for American Wire Gauge, is a standardized system used to denote the size or diameter of enameled wires. In this blog, we will delve into the significance of AWG in enameled wire and explore its applications in various industries.
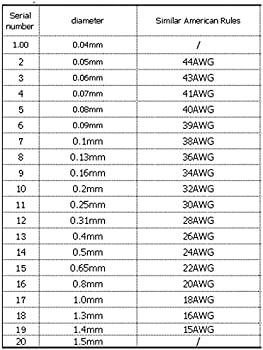
American Wire Gauge (AWG):
The American Wire Gauge system, commonly known as AWG, is a standardized method used to measure the size of wires, including enameled wire. AWG assigns a specific numerical value to each wire size, with smaller numbers indicating thicker wires. For enameled wire, AWG provides a standard reference for manufacturers, engineers, and technicians to determine the appropriate size and specifications required for specific applications.
Wire Size and Electrical Resistance:
In enameled wire applications, the wire's size plays a critical role in determining its electrical resistance. Thicker wires (lower AWG numbers) generally have lower electrical resistance, allowing for the efficient transmission of electric current. This is crucial in applications where minimizing power loss and maximizing conductivity are essential, such as motors, transformers, solenoids, and various electrical equipment.
Coil and Transformer Winding:
Enameled wires are commonly used in coil winding and transformer applications. The AWG designation helps manufacturers select the appropriate wire size for winding coils or transformers with specific voltage, current, and thermal requirements. By using AWG as a reference, they can ensure the wire's diameter is suitable for the intended application, preventing issues like overheating or inadequate electrical performance.
Space Constraints and AWG Selection:
In compact electronic devices or intricate machinery, space constraints often necessitate the use of
enameled wires with smaller diameters. The AWG system provides a wide range of sizes, enabling engineers to select thinner wires (higher AWG numbers) that meet the electrical requirements while fitting within the available space. This flexibility in wire size selection ensures efficient design and functionality in tight configurations.
Wire Insulation and AWG Compatibility:
In enameled wire, the insulation layer is crucial for electrical safety and preventing short circuits. The AWG system also ensures compatibility between the wire's insulation thickness and the corresponding wire diameter. Manufacturers follow AWG standards to ensure proper insulation thickness based on the wire size, maintaining the electrical integrity and insulation properties of enameled wire.
Repair and Replacement:
AWG becomes especially relevant during repairs or replacements of enameled wires. When damaged wires need to be replaced, technicians refer to the original wire's AWG size to ensure compatibility and proper electrical characteristics. This ensures that the replacement wire has the same diameter and insulation thickness, maintaining the desired electrical performance.
Conclusion:
AWG, or American Wire Gauge, plays a crucial role in enameled wire applications. From determining wire size and electrical resistance to guiding coil winding, transformer design, and accommodating space constraints, AWG provides a standardized system for selecting the appropriate wire diameter and insulation thickness. By understanding the significance of AWG in enameled wire, manufacturers, engineers, and technicians can ensure optimal electrical performance, safety, and compatibility in various industries where enameled wire is used.
